Centrifuges

A centrifuge is a laboratory apparatus separating fluid (gas or liquid) depending on density. Separation is accomplished by spinning a vessel containing material at high speeds; the centrifugal force propels heavier materials to the vessel’s exterior. Most laboratories, from academic to clinical to research, employ this apparatus to purify cells, subcellular organelles, viruses, proteins, and nucleic acids. Centrifuges are classified into categories based on their intended function or rotor design. Numerous types of centrifuges are available to researchers, ranging from enormous floor models to microcentrifuges.
PicoWay comes in 2 different configurations to best complement your practice
For Aesthetic:
The ultimate PicoWay device configuration for aesthetic and dermatologic needs features:
- Resolve Fusion 532 nm
- Resolve 1064 nm
- 730 nm
- Zoom 532 nm and 1064 nm
For Tattoo:
The premier PicoWay system configuration for tattoo removal features:
- 730 nm
- 785 nm
- Zoom 532 nm and 1064 nm
How PicoWay Works
Split-beam treatments include PicoWay Resolve and PicoWay Resolve Fusion. These minimally invasive procedures are popular for treating acne scars, wrinkles, and benign pigmented lesions.
Here are four big reasons our patients will love you for using the PicoWay system:
- Clinical evidence
Studies have shown that PicoWay lasers can deliver
- Reduced acne scarring after just three treatments
- High rates of improvement in wrinkle appearance
- A high rate of benign pigmented lesion clearance
- Removal of multi-colored tattoos
- Comfort
The PicoWay system uses a well-tolerated approach to building new collagen and elastin to treat acne scars and wrinkles.
- Low to no downtime
In brief, 15- to 20-minute treatment sessions, PicoWay Resolve treatment transforms skin while leaving the epidermis intact.
- Photoacoustic effect:
Its photoacoustic impact minimizes the risk of skin heating and damage to surrounding tissue.
Before and After
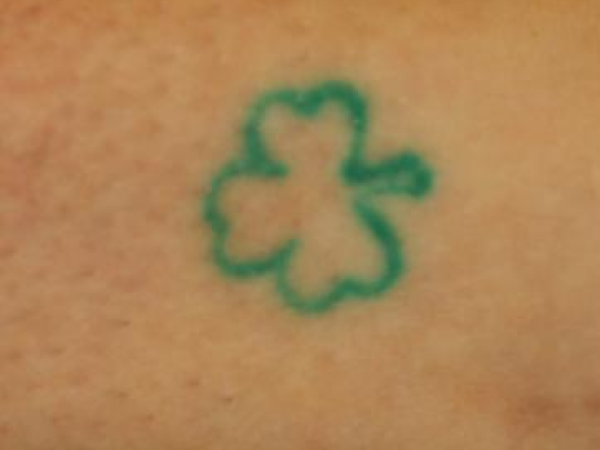
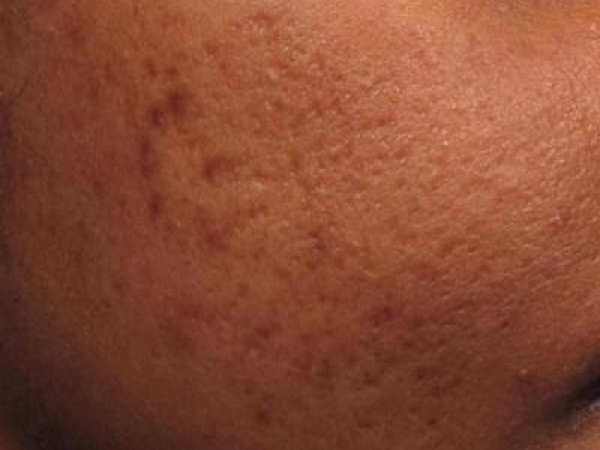
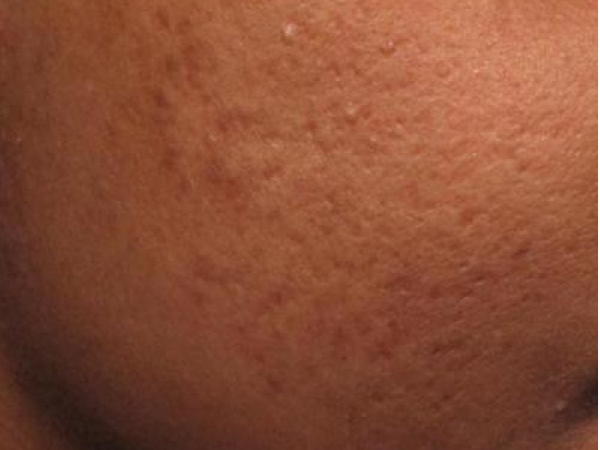

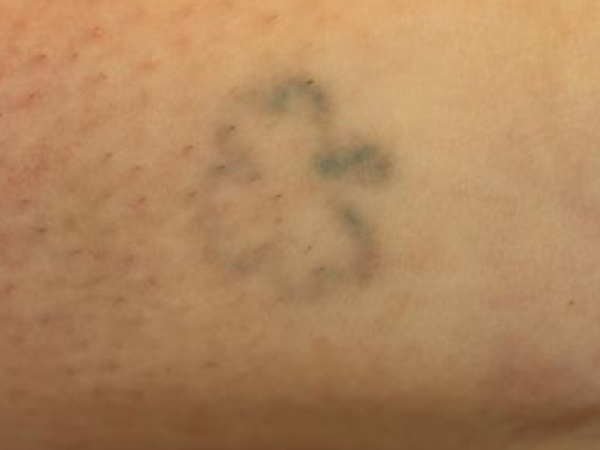
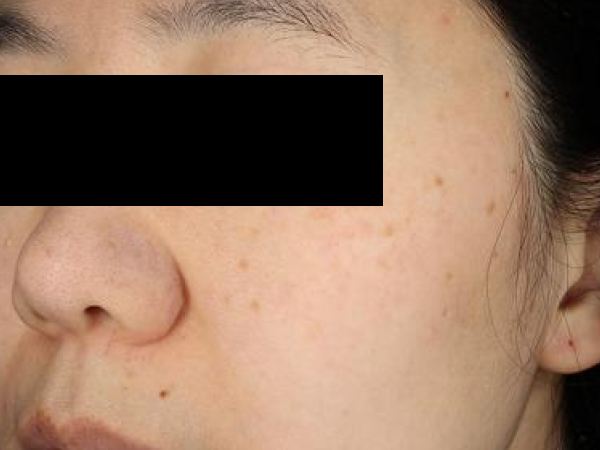
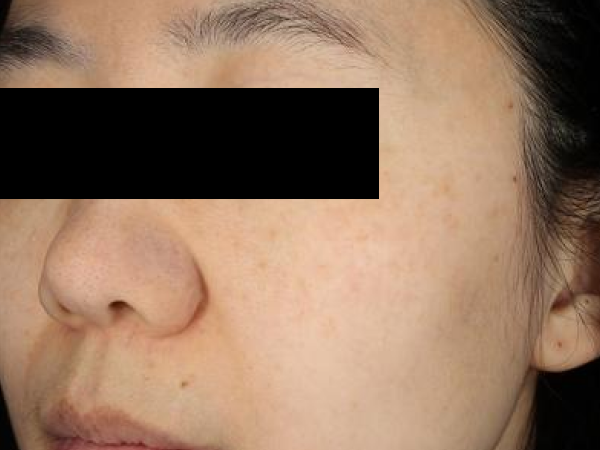
What is a centrifuge?
A centrifuge is a machine that employs centrifugal force to separate the contents of a sample according to density. When the centrifuge spins, it generates a significant centrifugal force. Though separation occurs naturally with Earth’s gravity, the centrifuge machine provides quick results for laboratory and other uses.
Centrifuges are classified into many different categories based on their intended application and rotor design. Centrifuge types include:
- Benchtop centrifuge
- Microcentrifuge
- Floor-standing
- Features include large capacity, STAT, refrigeration, high speed, and an ultracentrifuge.
What is centrifugation?
Centrifugation is the technique of concentrating natural forces acting on all particles of varying densities to speed the natural separating process. It is responsible for separating particles in the test tube based on their density. Centrifugation can be performed using either filtration or sedimentation processes. Filtration employs a mesh screen to retain the solid components while allowing the liquid components to pass through. Centrifuged blood samples cannot be filtered because the blood components are too tiny.
The particles are suspended in liquid and separated using a centrifuge machine in either process. Centrifugal force causes things to separate, pushing them outward towards the tube’s tip.
Centrifugal Principles:
Centrifugation is fundamentally a sedimentation-based separating process. Denser particles settle to the bottom of the container, while lighter particles remain floating. Centrifugation displaces particles with even modest differences in density and is governed by these four factors:
- The density of the samples and solution.
- Temperature and viscosity
- The distance that the particles are moved
- The speed of rotation
Relative centrifugal force (RCF), often known as G-force, is the amount of acceleration delivered to the sample. When RCF surpasses the buoyant and frictional forces in the sample, the particles migrate away from the axis of rotation, causing sedimentation.
What is a Centrifuge Used For?
Centrifuge machines are commonly used in laboratories to isolate specific biological components for testing due to their ability to separate particles by density. For example, a blood sample has red blood cells and plasma. After centrifugation, the red blood cells will be at the bottom of the tube, while the plasma will be on top.
Centrifugation is required to study specific components, such as separating blood plasma for testing, isolating DNA, or even separating urine sediment.
How Do Centrifuges Work?
The centrifuge machine replicates and accelerates centrifugation to separate components in a sample. Because of the forces involved, these devices are meticulously built to function effectively while keeping the operator safe.
Parts of the Centrifuge Machine
A robust motor in the center generates The centrifuge’s spin. The rotor is attached to this motor and will rest on the containers carrying the tubes containing the material to be centrifuged. These containers can be spun at 45 degrees (fixed angle centrifuge), 90 degrees (horizontal centrifuge), or no angle (vertical centrifuge).
Depending on the centrifuge, the tubes can be loaded at the angle at which they will rotate or into a container that will automatically shift to a different angle upon startup. This second methodology, swing bucket, is standard in horizontal centrifuges.
Depending on the centrifuge used, a range of controls may be available. Some centrifuges are pre-programmed with one, two, or three processing options. Some have a digital display that allows for comprehensive customization. When you start the centrifuge, regardless of the control type, the motor will run according to the settings you provide. During the cycle, the sample in the test tubes separates into its many components, making it available for examination.
How To Use A Centrifuge Machine
Despite the centrifuge’s sophisticated principles, running it is quite straightforward. To operate a centrifuge machine:
- Insert the test tube sample in one of the portals.
- If necessary, insert test tubes filled with water for balance based on the quantity of samples you are testing.
- Secure the lid and select the desired settings.
- Start the centrifuge and wait for it to complete its cycle.
- Once the centrifuge has stopped spinning, remove the balances and samples.
- Each sample will now be divided into its constituent components and prepared for analysis.





